
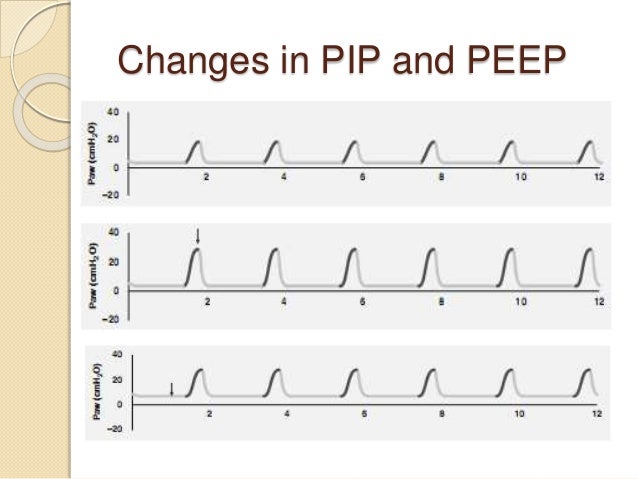
High Raw curve – A significant increase in the PTA is associated with increased airway resistance. Normal curve – demonstrates normal PIP, Pplat, PTA (transairway pressure), and Ti (inspiratory time).

PRESSURE-TIME CURVES SHOWING PIP AND PLATEAU PRESSURES IN VOLUME CONTROL VENTILATION High alveolar pressures can be due to excessive tidal volume, gas trapping, PEEP or low compliance as shown by this relationship:Īlveolar pressure = (volume/ compliance) + PEEP.To prevent lung injury, alveolar pressure (aka the plateau pressure) should be kept
#Pip in mechanical ventilation full#
Because flow is reduced to zero, airway pressure and alveolar pressures will equalise and the airway pressure will correspond to the alveolar pressure at full inspirationĪirway pressure = 0 x resistance + alveolar pressure = alveolar pressure.
The inspiratory pause pressure is determined by observing the plateau pressure in an apneic ventilated patient when when the ‘ inspiratory pause hold‘ control is activated.Alveolar pressure is estimated by determining the inspiratory pause pressure, which corresponds to the plateau pressure.A maximum acceptable PIP of Peak inspiratory pressure (PIP) is displayed on most ventilators.Airway pressure is more conveniently measured than alveolar pressure.Thus if flow or resistance is markedly altered, a change in airway pressure will not be indicative of a change in the alveolar pressure.It is important to distinguish between airway pressure and alveolar pressureĪirway pressure = flow x resistance + alveolar pressure indicate an equipment problem that needs to be addressed.indicate a deterioration of the patient’s condition.High airway pressures are important because they may:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
